
In industrial computing, storage technology must do more than deliver high performance—it must remain reliable over time, in challenging environments, and under continuous load. U.2, a high-speed storage interface developed with enterprise needs in mind, continues to be a trusted solution in rugged systems where endurance and serviceability are essential.
But as the industrial edge expands—and systems become smaller, smarter, and more power-conscious—another interface is taking on a central role: M.2. With its compact footprint and growing capabilities, M.2 is shaping the future of industrial storage in a wide range of embedded and edge applications.
U.2: Proven Reliability in Demanding Conditions
U.2 (formerly SFF-8639) is a PCIe and NVMe-based interface that connects to SSDs using a 2.5-inch form factor. Its cabled design allows the drive to sit away from the motherboard, creating more space for airflow and reducing thermal pressure inside the system enclosure.
This layout offers a clear advantage in environments with extended operating cycles or elevated temperatures. U.2 drives also support higher power envelopes, making them suitable for high-capacity, high-endurance SSDs built to withstand sustained workloads.
Serviceability is another key benefit. U.2 drives are hot-swappable, allowing field technicians to replace or upgrade storage without shutting down the system—minimizing downtime in mission-critical environments like factory automation, industrial control systems, and field servers.
SSD Form Factors

Source: Toshiba
Side-by-Side Comparison
| M.2 Storage | U.2 Storage | |
|---|---|---|
| Form Factor | Compact card, mounts directly to motherboard | 2.5” SSD with cable connection |
| Interface | PCIe/NVMe or SATA | PCIe/NVMe |
| Max Lanes | Up to 4 PCIe lanes | Typically 4 PCIe lanes |
| Hot-Swappable | No | Yes |
| Thermal Management | May require a heat sink | Better airflow and heat dissipation |
| Serviceability | More challenging to access, replace | Easy swap with standard drive bay |
| Power Envelope | Lower (common for embedded use) | Higher (supports power-hungry drives) |
| Use Case Fit | Compact systems, edge AI, IoT | Data intensive, industrial, ample power |
M.2 vs. U.2: A Matter of Design Intent
While U.2 focuses on serviceability and thermal headroom, M.2 offers a streamlined approach to storage integration. Designed to mount directly to the motherboard without cabling, M.2 enables compact system layouts and supports both SATA and NVMe protocols.
In terms of raw performance, M.2 and U.2 can offer similar throughput when using PCIe-based NVMe SSDs. The differences come down to design requirements: U.2 lends itself to larger systems with more space and airflow, while M.2 fits naturally into smaller, more integrated platforms.
Both have their place. U.2 remains a strong fit for high-availability environments, while M.2 aligns with modern trends in industrial design—where devices are becoming more compact, more power-efficient, and more distributed.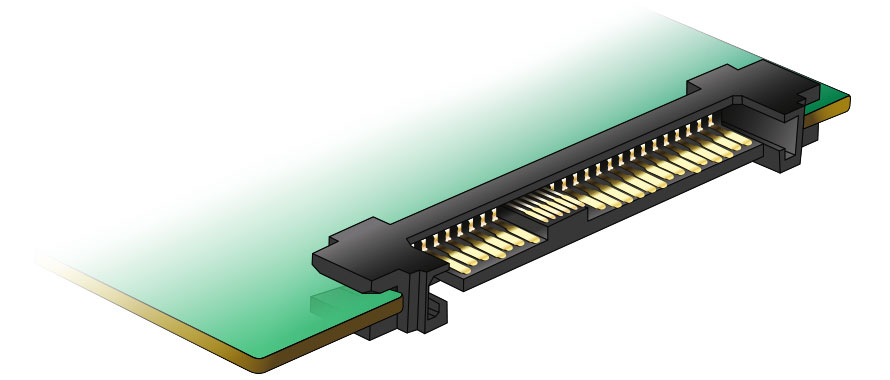
U.2 Connector (Source: https://www.delock.com/)
M.2 for the Evolving Industrial Edge
M.2 is increasingly favored in industrial PCs, edge AI systems, robotics, and embedded platforms. Its compact footprint allows for tight integration without sacrificing speed, and its low power draw supports efficient system operation in remote or power-sensitive installations.
Advances in heat management—from improved heatsinks to enclosure-level airflow optimization—have addressed earlier concerns around thermal performance, making M.2 viable even in demanding applications.
As edge computing becomes more central to industrial operations, the ability to embed high-performance storage directly into compact systems is a significant advantage. M.2 enables fast local data processing, rapid boot times, and simplified system design—all critical for next-generation industrial applications.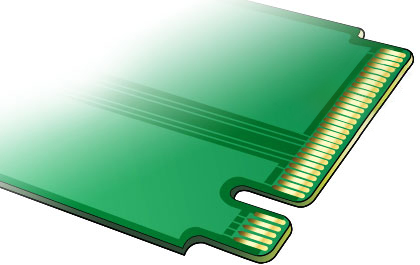
M.2 Connector (Source: https://www.delock.com/)
Conclusion
U.2 continues to be a valuable storage solution in industrial systems that demand high endurance, field-replaceability, and stable thermal performance. It’s a reliable option for applications where system uptime and long-term serviceability are critical.
At the same time, M.2 offers a compelling path forward. Its performance, efficiency, and small form factor make it well-suited to the evolving demands of modern industrial computing. As systems become more distributed, compact, and intelligent, M.2 is emerging as a key enabler—delivering the performance needed without adding unnecessary complexity or bulk.
Both interfaces have strengths. The right choice depends on the system architecture, deployment environment, and long-term maintenance goals. But as the edge continues to grow, M.2 is increasingly positioned to meet the needs of what comes next.
Need help evaluating your industrial storage requirements? Let’s talk. At CoastIPC, we live at the edge of industrial computing performance. Our experts are ready to discuss any storage technology. Contact us anytime via email, phone, or chat. Sign up for our blog or follow us on LinkedIn to learn more about our industrial computing solutions.
